A body paint should always be ordered in professional quality. The cost of the paint is certainly double that of a paint that can be found on the market for the general public, formulated according to the color codes of German cars and among them, the color codes of Volkswagen cars. But the quality will be much better, as well as the durability, and above all, what is most important, there will be no problems during the application.
Ordering professional quality Volkswagen color code paint actually saves a lot of time and hassle.
Painting on a Volkswagen vehicle can be carried out by the professional body painter (consult them for a quote – this painter may offer to provide the paint, but be aware that this paint will be sold for more than on our site and above all, you will be provided with a water-based paint, which is much less durable than the solvent-based paints that we offer).
It is also possible to do the painting yourself, especially when you have a small area of the bodywork to repaint. It can be a rear view mirror up to parts as big as a bumper or a door.
For paint users who have a spray gun, we offer paint pots and we also fill aerosols for those who do not have a paint gun.
Important : modern automotive paints are supplied in 2 forms :
• “direct gloss” paints, in a complete kit, with hardener, paint and thinner (this concerns only old colors and in general, all colors that do not contain mother-of-pearl or metal)
• “matt base” paints, which are single-component paints, easy to apply and which have represented most automotive colors for the past twenty years.
Volkswagen car color codes
Here is a quick summary of the different steps you will have to perform to paint your touch-up on your Volkswagen car. Of course, we strongly invite you not to limit yourself to this simple information, as well as to reading the label present on the way of painting, but to read absolutely all the indications, advice and instructions present on the page. of the product.
The preparation of the surface before painting allows the success of the painting at 80%. The remaining 20% are just a few simple execution gestures. The first step is therefore the preparation of the support :
We are not talking here about the ration of shocks which require a rectifier of the sheet, or the application of a putty, with a filling primer.
In the case of large and deep scratches : yes, it is necessary to apply a filler to fill in the scratches. Applying a primer is not enough. This product, which can also be called primer filling surfacer, must be applied to sanded putties or fine scratches, before painting.
Please note, depending on the Volkswagen color code that you order, it is sometimes necessary to have a primer of a certain color (white or black, sometimes certain shades of gray), but in general, a gray primer is enough.
If your Volkswagen car simply has fine scratches or just a color faded by the sun, the preparation will only consist of a light sanding of the old varnish, in order to allow the paint to adhere. Sanding can be done with a 500 grit.
The application of Volkswagen paint, which has been formulated according to the exact color code (provided by you when ordering), is done with a spray gun after dilution, unless you buy the small formats which are already diluted . Apply the paint in a few very thin coats and go straight on with the varnish, without waiting more than 30 minutes, to allow a "wet on wet" grip.
The varnish is mandatory in the case of matt base paints. Today, almost all metallic pearlescent paints are two-layer paints (base + clearcoat). The varnishing is a delicate step that will crown all the efforts made. The secret of varnishing is the application of the right dose of varnish, in 2 very shiny coats spaced 2 minutes apart. If the layer is too thick and the temperature is low, the paint will run. If the layer is too thin and the temperature is too hot, the varnish then forms a defect called "orange peel".
The history of the Volkswagen manufacturer
The history of the Volkswagen brand may surprise you. This brand of German car manufacturer was created about forty years after the appearance of the first car manufacturers in Europe or the United States. It was during the Nazi Party era (1937) that the impetus for the creation of this constructor was born.
In the German language, Volkswagen means the people's car, which clearly shows, from the outset, the intention and objective of the project, which is to provide affordable passenger cars for as many customers as possible, and not for a privileged clientele or an elite.
Volkswagen was not applied for example in motor racing as the main car manufacturers were during the 20th century (Mercedes, Ferrari, Renault, Jaguar, Bugatti).
The first Volkswagen strangely resembled Citroën's 2 CV. The models were designed by a team of designers whose primary ambition was to create smaller and ever more affordable vehicles. It was also the ambition of the German Führer Adolf Hitler who participated in the orientation of the management of the manufacturer: the latter wanted each German family to be able to get a car and move up to speeds of 100 km/h.
During the difficult period of the Second World War, the Volkswagen factories were entirely at the service of the German war effort. Many prisoners in the camps are forced to work in car factories. We are talking about 15,000 slaves today. Following legal action, the German firm had to create a compensation fund for the victims of this slavery in 1988.
After the war, the Volkswagen brand was already a globally recognized brand, as well as a solid company and powerful. Thus, it conquers the American markets where it meets with great success. It is then around Canada where it builds giant factories. In 1960, it was in Brazil that Volkswagen firmly established itself with the creation of a factory. The bad reputation gained during the second war continues the brand, with accusations of partnership with the Brazilian dictatorship during the 1970s. This is the date on which the first Golf will come out, with worldwide success.
The emblematic model of the brand is the Beetle, all brands and all years combined.
In 2010, the German brand set a new record for vehicle sales in a single year : nearly 6.3 million vehicles sold.
Today, Volkswagen has become the world's largest car manufacturer and most of its sales (about 40%) are made in Asia, especially China.
Where to find the color code of your Volkswagen car ?
How to find your Volkswagen paint color code ?
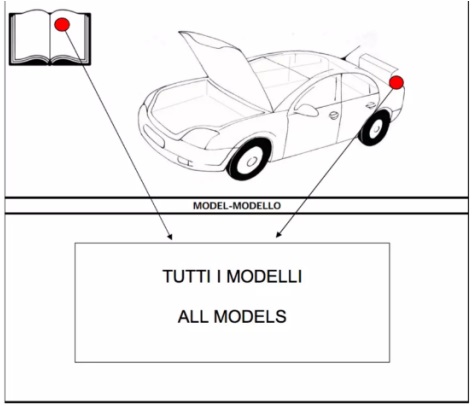
A color code is a series of letter numbers. It is always found, whatever the brands, not on the vehicle's gray identification card, but on certain locations on the exterior or interior bodywork:
For VOLKSWAGEN brand vehicles, the plate mentioning the code color (vinplate) can be in two different places.
- In the spare wheel compartment Or in the boot.
- Printed on the car's service book.
You can take help from the images provided below which illustrates the location.
The color code is always composed of letters or numbers, but the number of characters that form the code is variable, it can be numbers such as up to 4 or 5 numbers.
2B2B AVOCADOGRUEN VOLKSWAGEN/AUDI 2005 - 2008
2C BLUE SILVER VOLKSWAGEN/AUDI
The iconic colors of Volkswagen cars
The color database is probably the largest in the world, ahead of Ford and Renault. In addition, the Volkswagen database for color codes is coupled with that of the manufacturer Audi.
Here are some examples of Volkswagen color codes :
2B2BBLUE SILKVOLKSWAGEN/AUDI 2012 -
3594 AZUL NAUTICO VOLKSWAGEN/AUDI 1995 -
3700 MERCURY SILVER VOLKSWAGEN/AUDI 2011 -
You can find, in a first column, the color code which is very variable.
Then, we find the name of the color, very important information, which is never present on the bodywork. Sort of secondary verification information for color manufacturers. This information is also known by the dealer.
We then find the brand and the year of appearance of the color.
Car color code BMW
Car color code Mercedes
Car color code Opel
Car color code Porsche
Car color code Smart
Audi car color code